GIS enables users to effectively investigate and analyze location-based data in three dimensions, and time adds a fourth dimension to this data. Time enabled data let’s users see what events occurred at a certain time, or what events may unfold in the future based on trends witnessed over time. Time-enabled data comes with added functionality within the ArcGIS platform, including ArcGIS Pro and ArcGIS Online.
Temporal data types can vary. Linear time is directional, meaning each moment is unique, and time moves forward. Cyclic time repeats itself, and time loops back around (like a daily exercise routine).
Space-time data helps monitor time-enabled features
Moving features – Animals, airplanes, vehicles, people, storms
Discrete events – Crime, accidents, lightning strikes, volcanic events
Stationary sensors -Weather stations, traffic sensors, stream gauges
Change or growth – Demographics, fire perimeters, flood extents
The Living Atlas offers many time-enabled datasets for easy visualization with a simple slider in ArcGIS Pro. Let’s leverage a time-enabled dataset available from the Living Atlas of the World. Our first example depicts internet usage per 100 population for each country around the world. Notice how the time-enabled combination of mapped data provides a deeper understanding of trends over time.
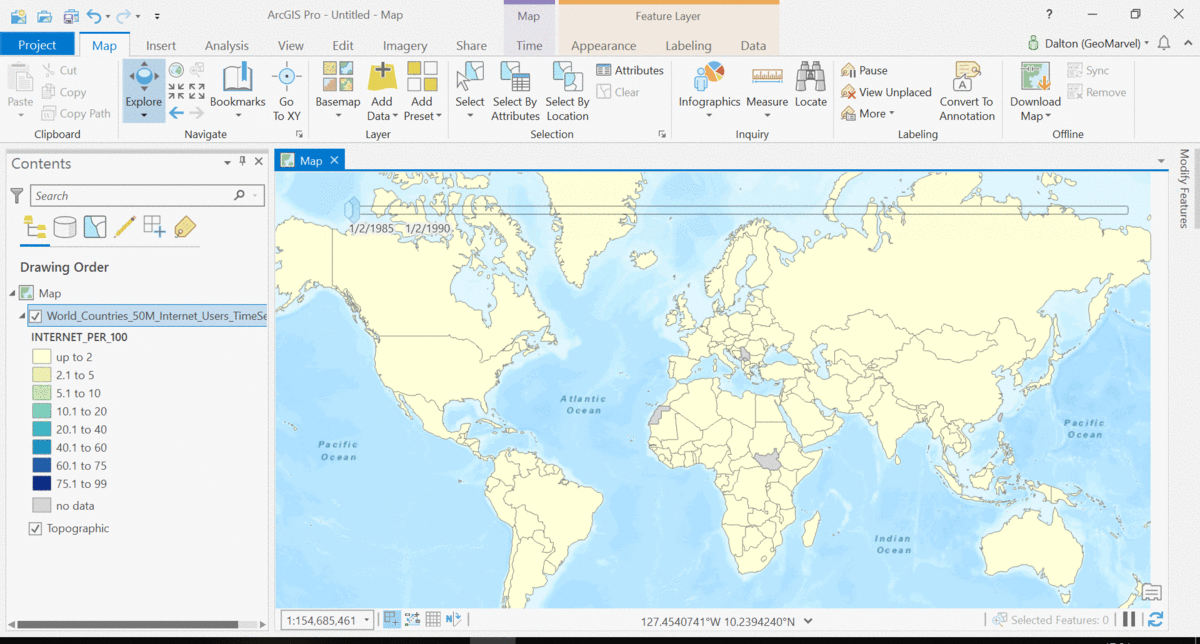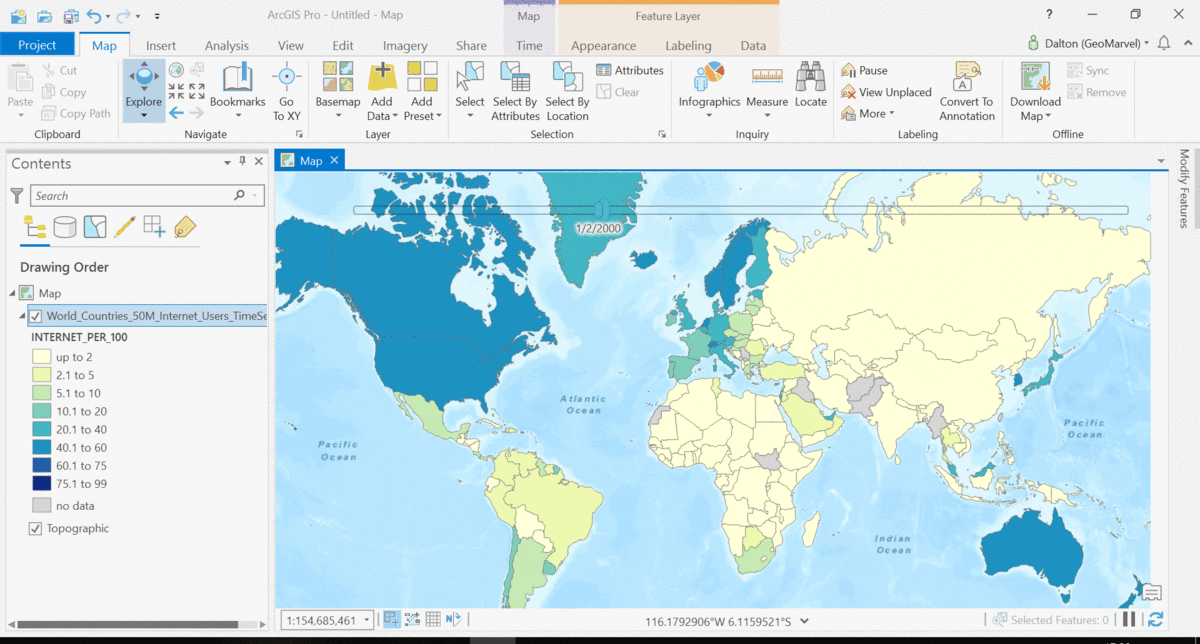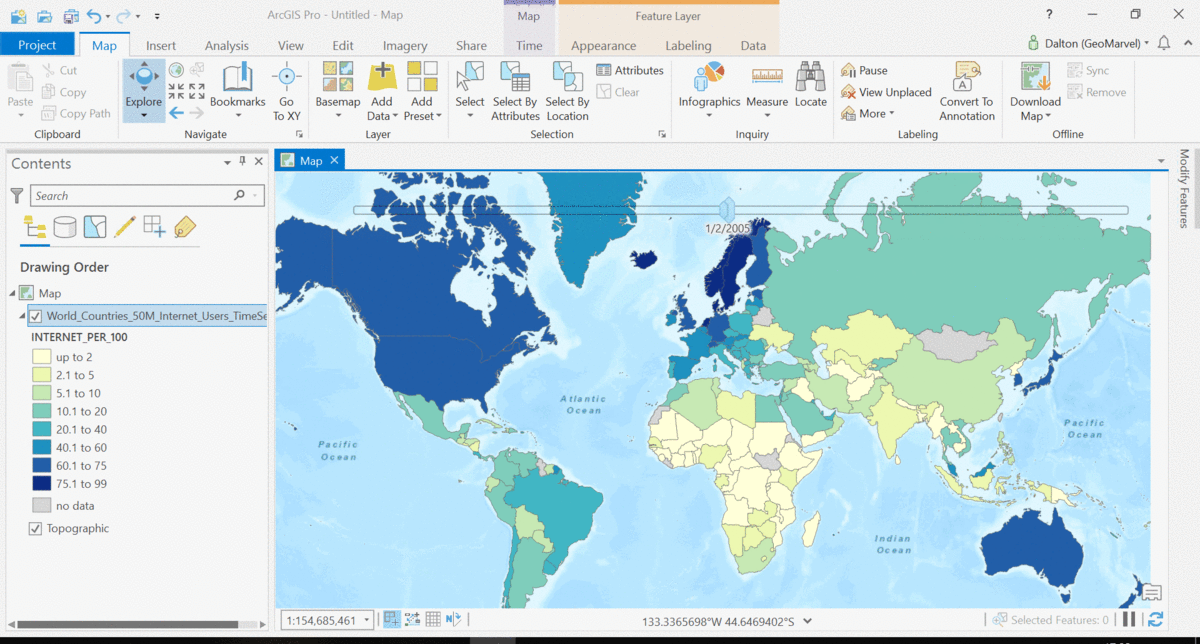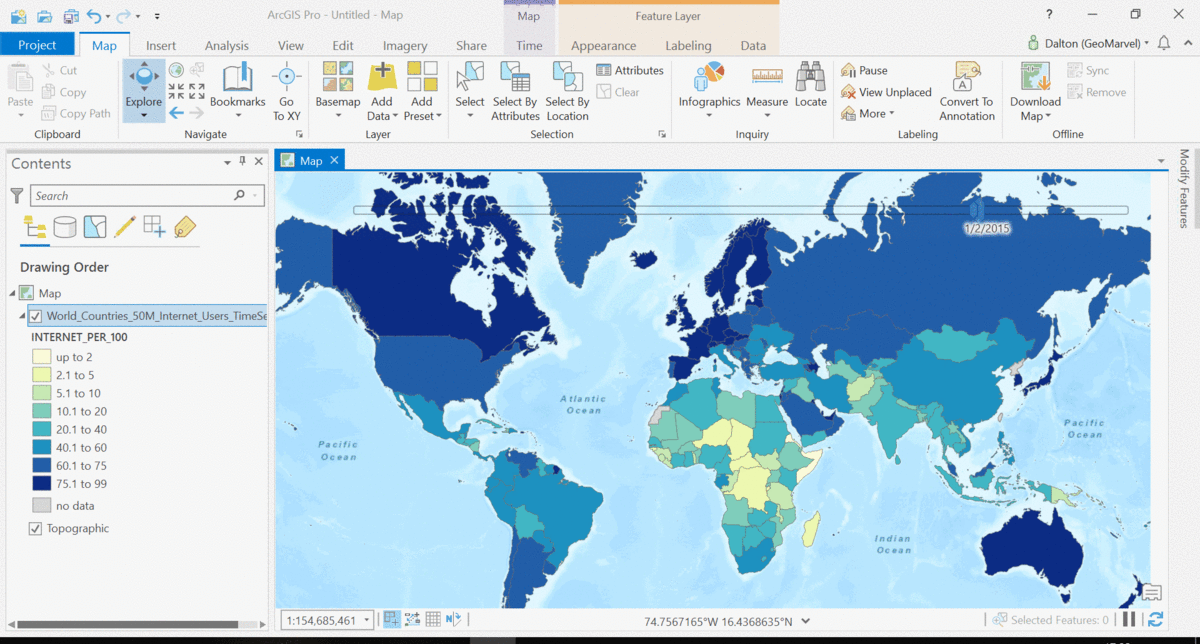
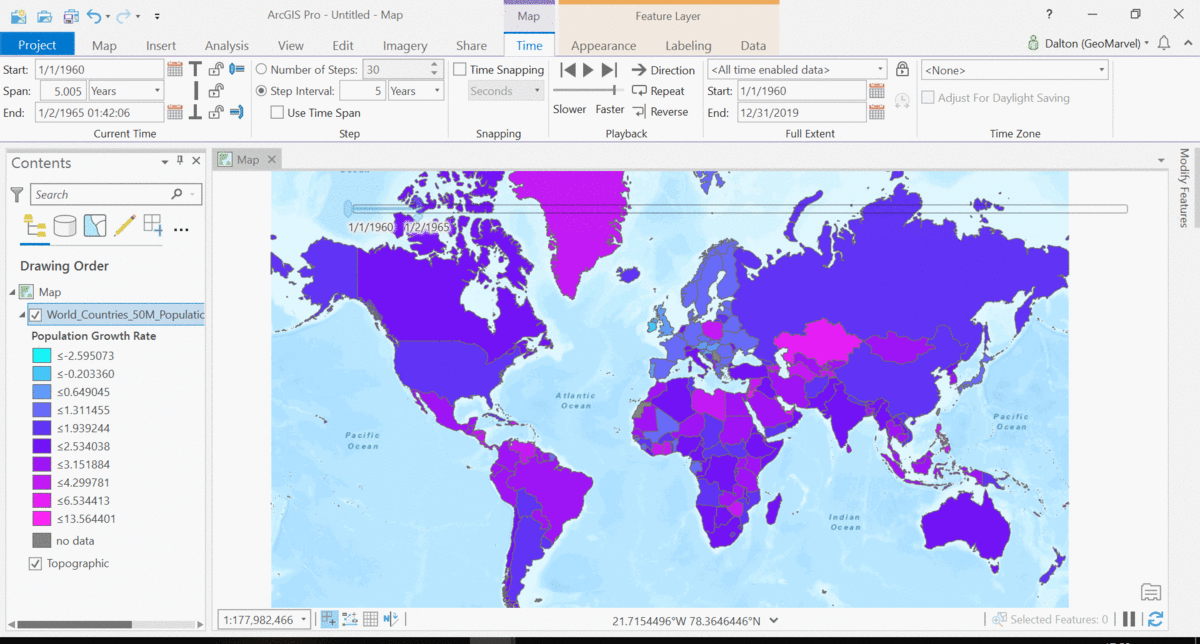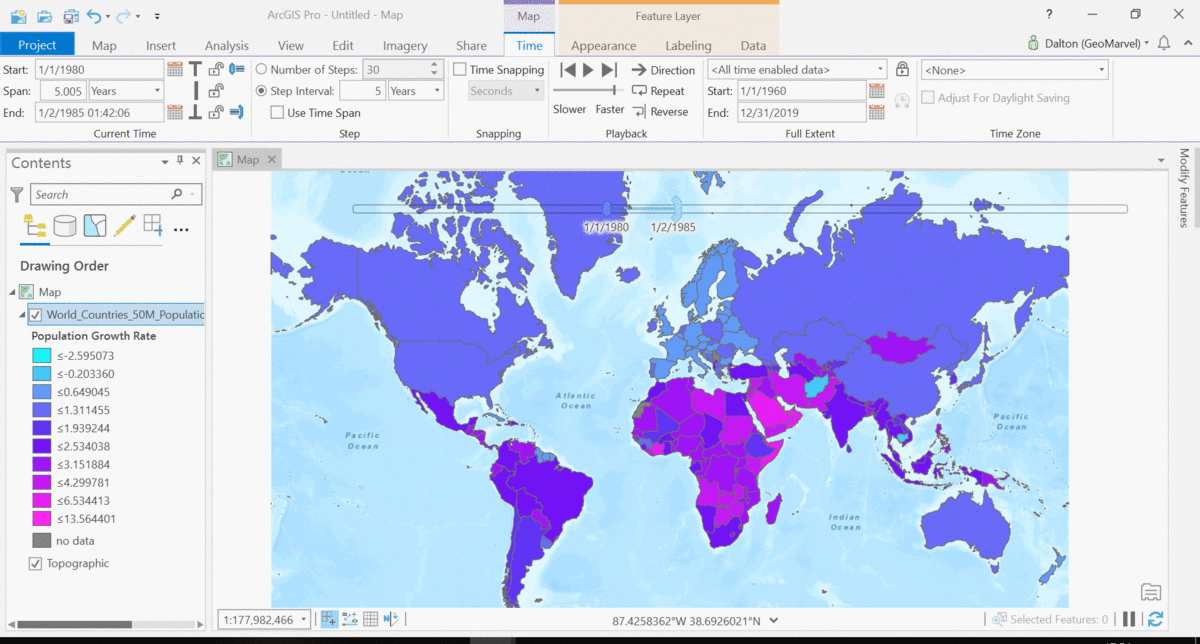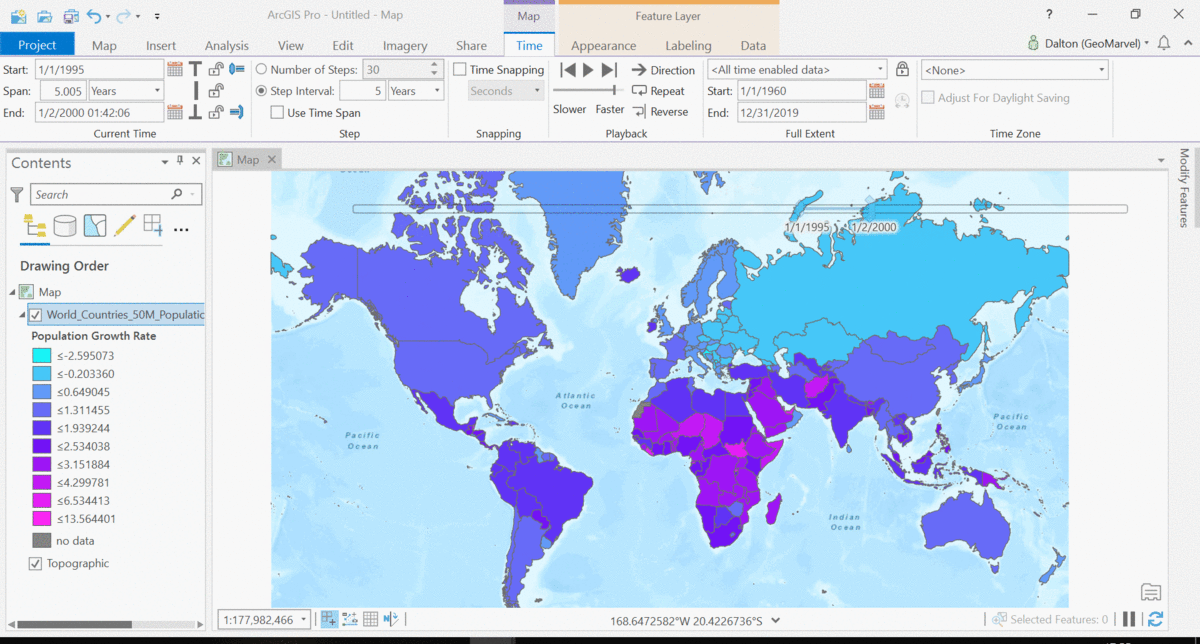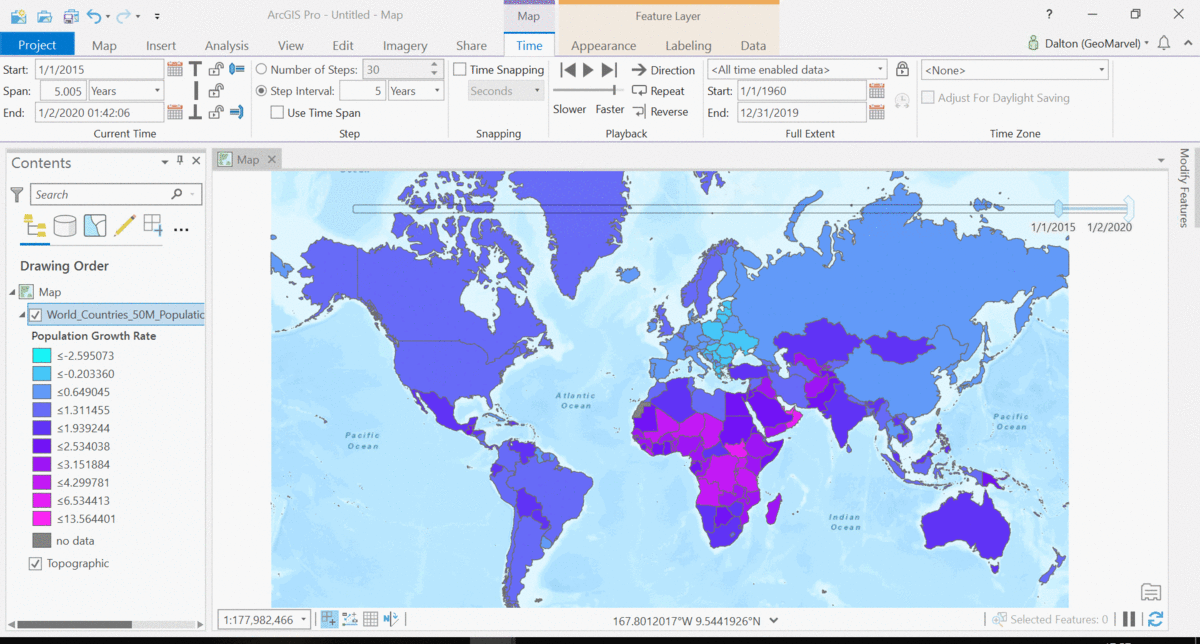
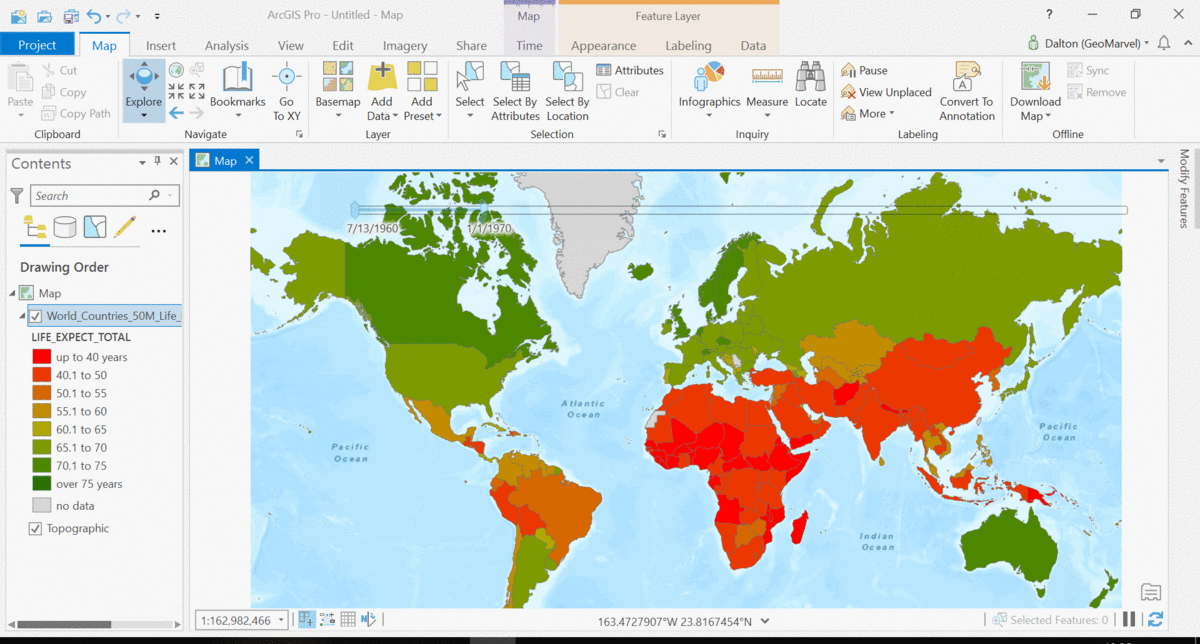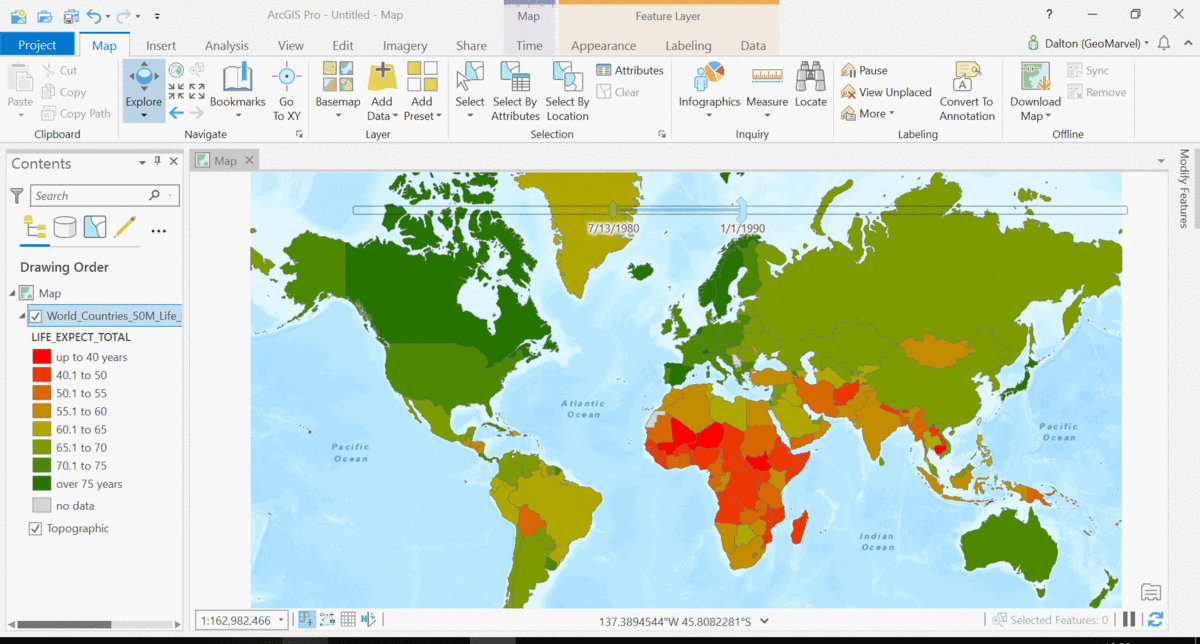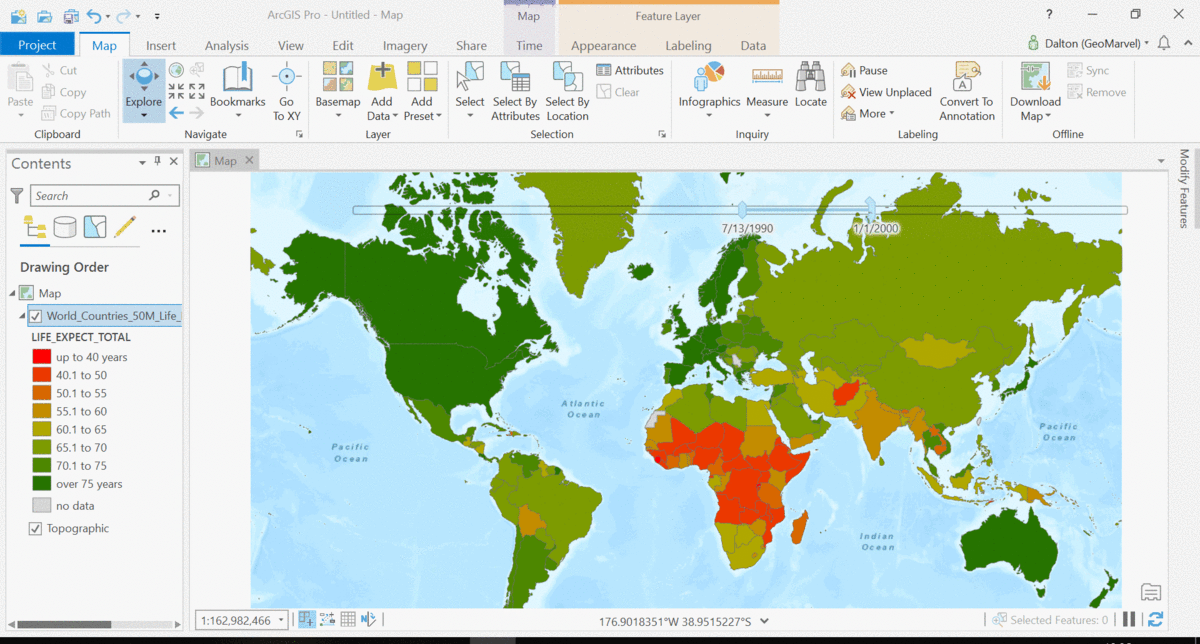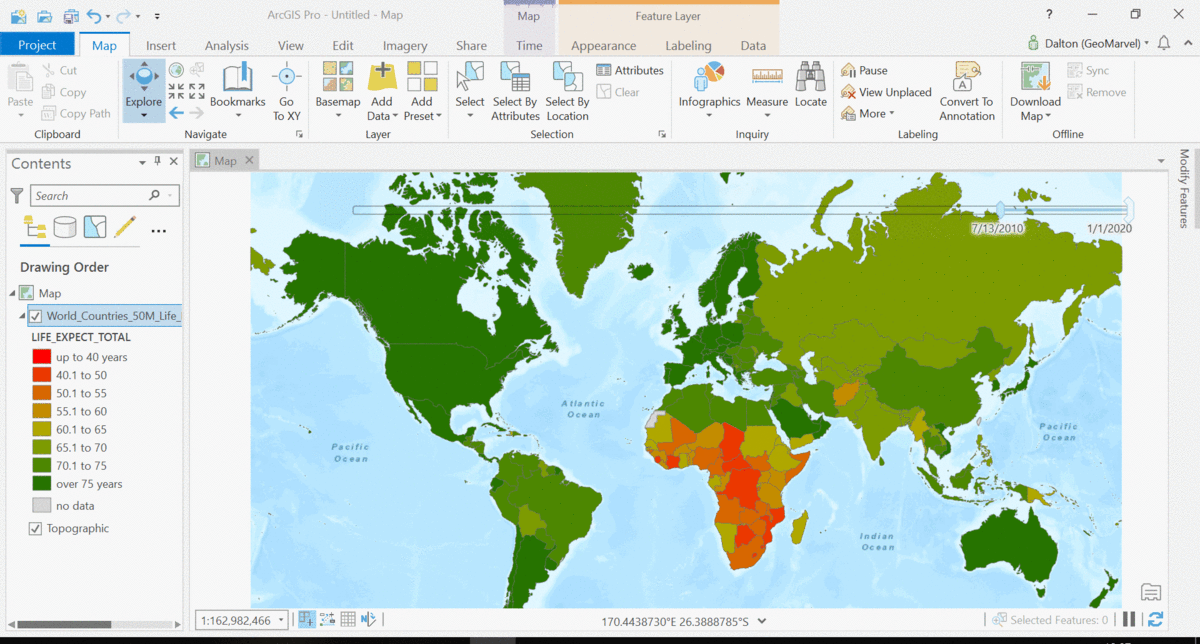
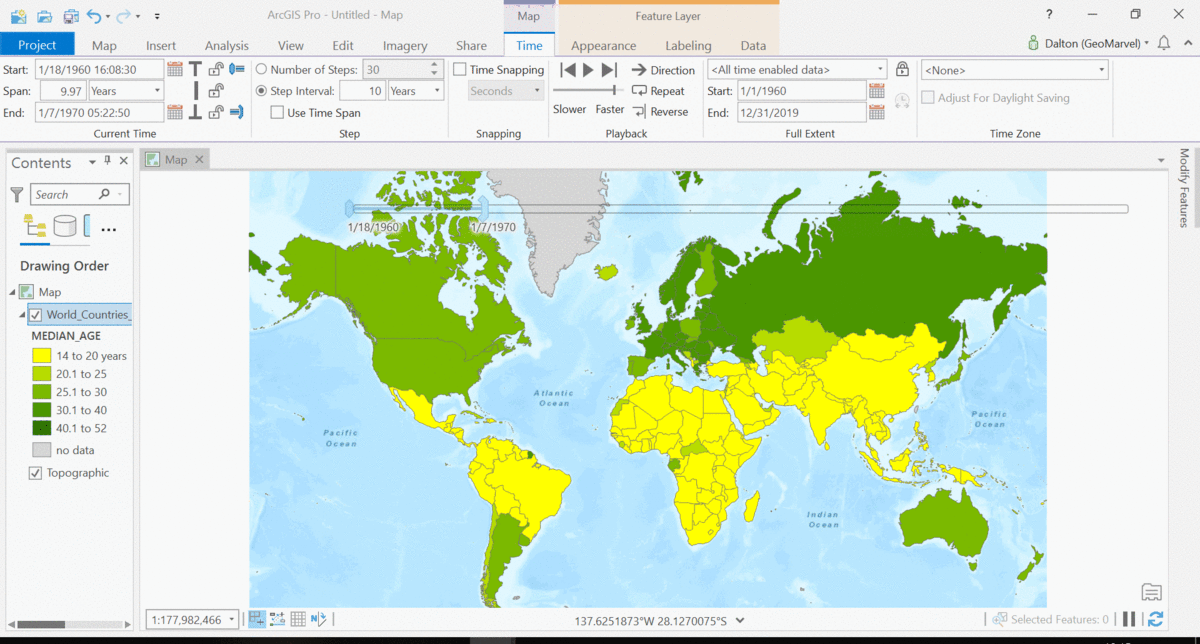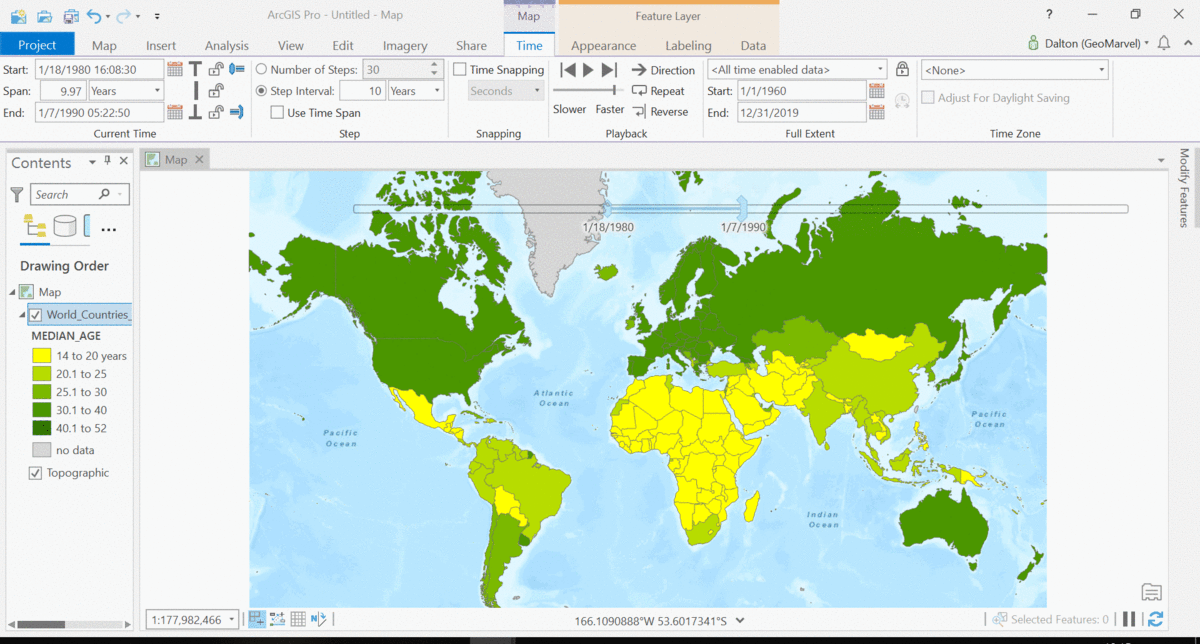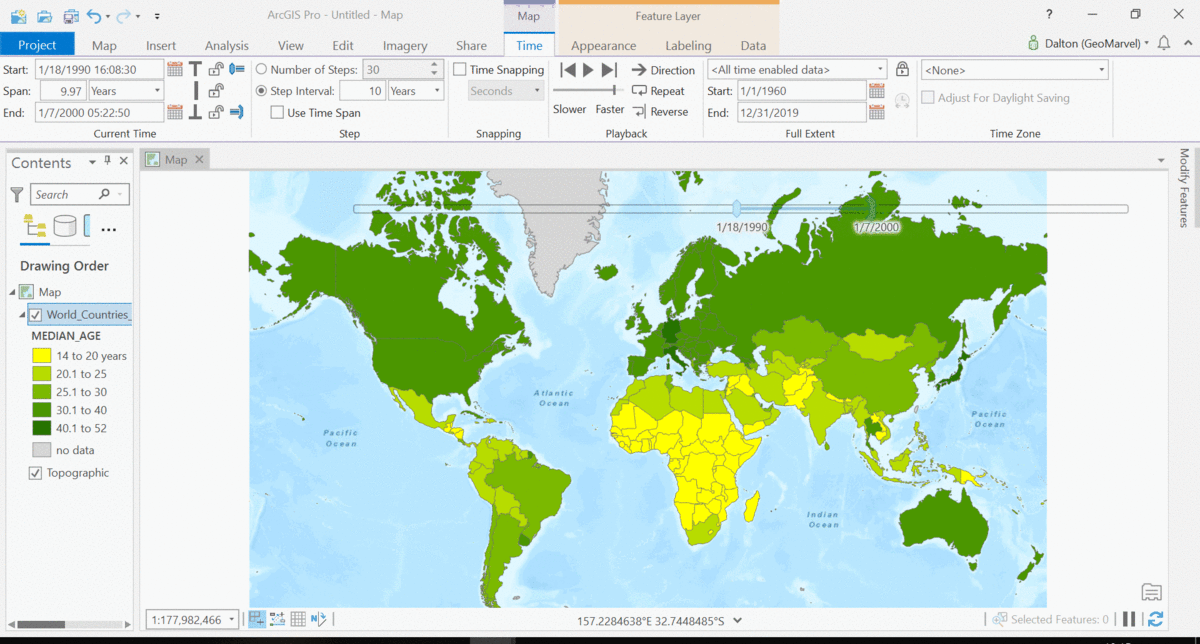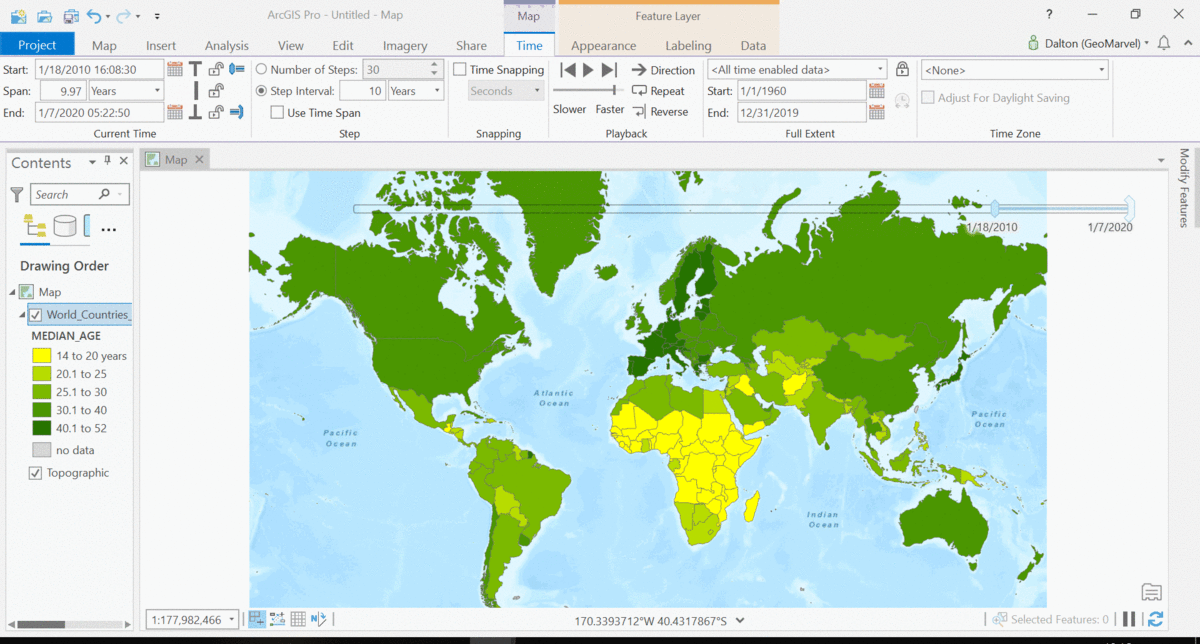
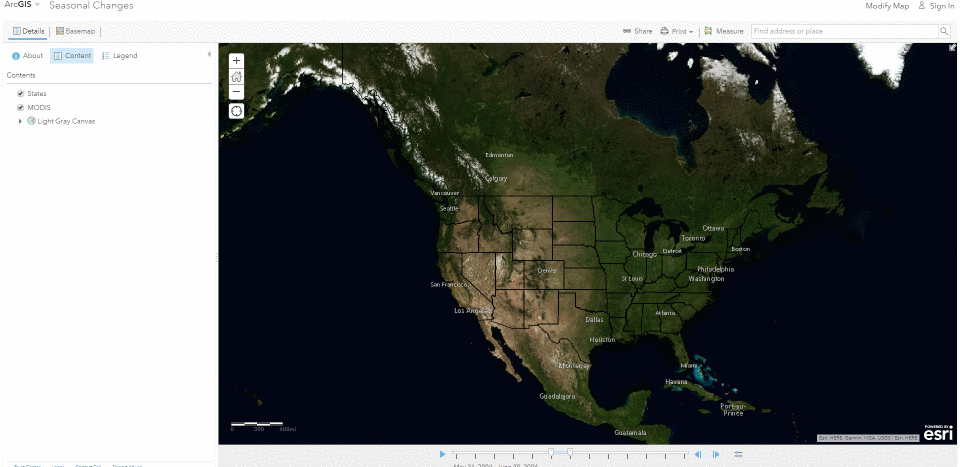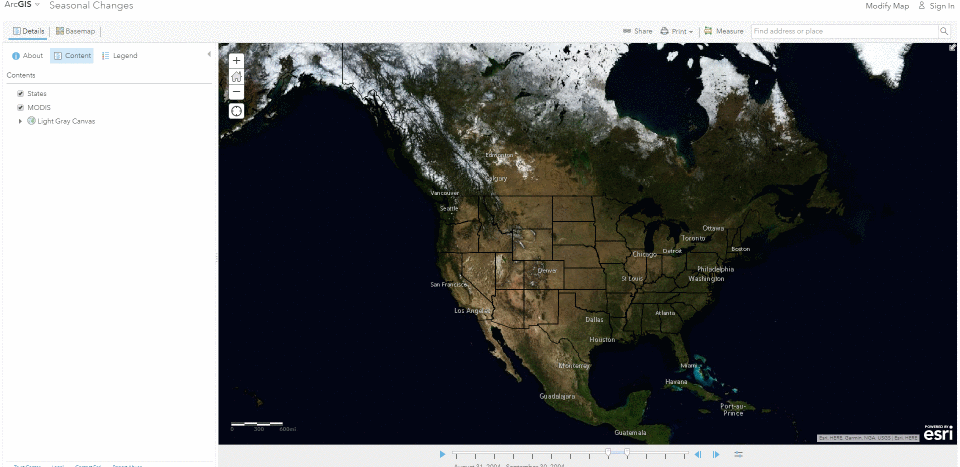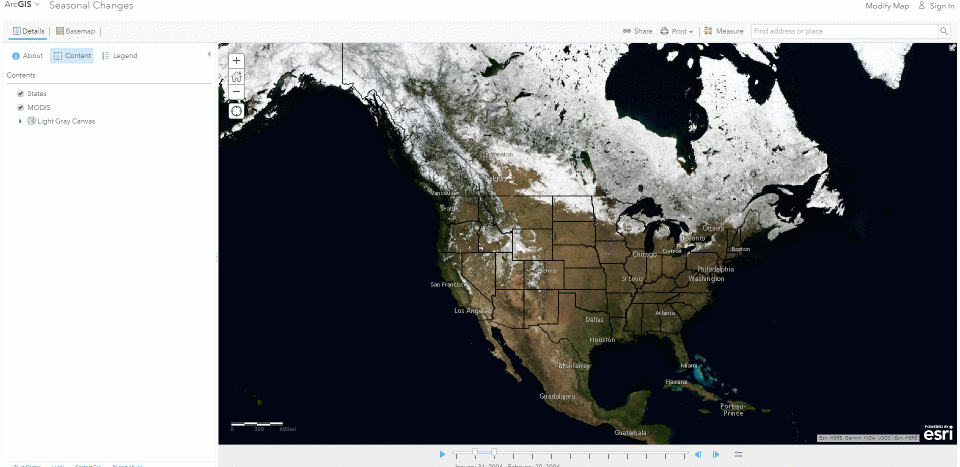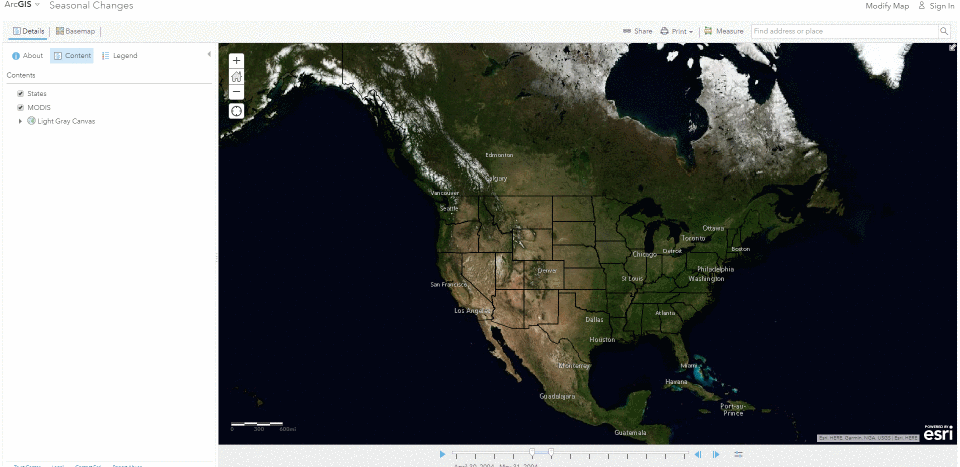
Temporal values best practices
Time values are best stored in a date field, which stores dates and times. Each time-enabled data entry should be contained in a single row of the table. And ensure all time values in this row are in the same time zone, using the “Convert Time Zone” geoprocessing analysis tool as needed.
Time adds another dimension to data, allowing for a deeper understanding of the trends in the data that emerge over time. The simple time slider allows for easy visualization of the data at equal time intervals. Oftentimes, data with a time aspect needs a little data clean up before it can be properly displayed as a time series. Learn how to transpose fields and properly structure your time data with this quick tutorial from esri.
Get Support
Discover GeoMarvel’s previous work in our diverse portfolio. Have a unique solution in mind? Reach out to our industry experts to start a conversation today.



