
In the world of GIS, efficiency, accuracy, and automation are paramount. One of the tools that make these goals achievable is ArcGIS Pro ModelBuilder. In our latest GeoMarvel Live demonstration, we explore the essential concepts and steps outlined by Keith Ornbaum, a Solutions Engineer at GeoMarvel, of ModelBuilder. ModelBuilder is a visual programming language that empowers GIS users to create geoprocessing workflows, automate tasks, and streamline data management processes.
ModelBuilder is essentially a diagrammatic representation of a workflow that chains together a sequence of geoprocessing tools and processes. These tools allow for the automation of complex spatial analyses and data manipulation tasks. The output of one process serves as the input to the next, creating a seamless flow of data and actions.
Before diving into the construction of a model, it is crucial to grasp the fundamental building blocks of ModelBuilder. Let us examine these four elements to gain a better understanding of their distinctive attributes:
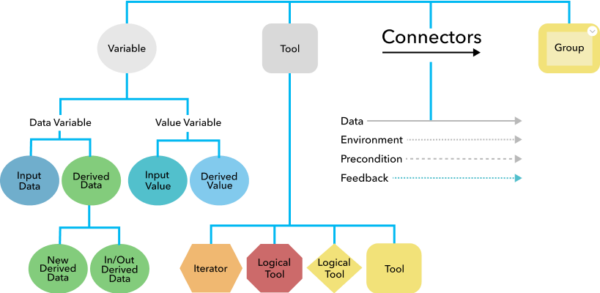
Model Elements in ModelBuilder
To illustrate the process of creating a ModelBuilder model, let’s break down the steps Keith outlined:
1. Select and Connect Data: Begin by dragging and dropping the required layers into the model. In the example provided, Keith needed to clip parcels based on an area of interest (AOI).
2. Add Geoprocessing Tools: Search for and add the necessary geoprocessing tools to your model. In this case, Keith used the “Clip” tool, followed by the “Add Field” and “Calculate Geometry” tools to meet the client’s requirements.
3. Configure Tool Parameters: After adding a tool, configure its parameters by connecting the appropriate variables and data sources. Ensure that all required variables are properly connected. A yellow tool icon indicates that all necessary variables are met.
4. Label the Model: Label each step of the model to provide clarity and documentation. This helps in identifying the purpose of each component in the workflow.
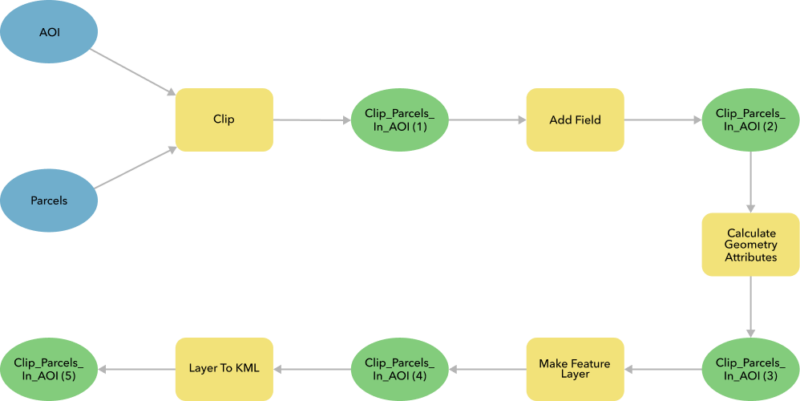
Model Diagram in ModelBuilder
5. Validate the Model: Before running the model, validate it to check for any issues such as missing or invalid parameters. Validation ensures that all processes are in a ready-to-run state.
6. Run the Model: Execute the model by clicking the run icon. Monitor the process, and if needed, specify the close-on-complete option to streamline the workflow.
ModelBuilder empowers GIS professionals to create efficient, automated workflows by visually connecting geoprocessing tools, variables, and data sources. This tool not only streamlines processes but also ensures reproducibility and documentation of spatial analyses. As GIS continues to play a vital role in various industries, ModelBuilder serves as a valuable asset for professionals seeking to harness the power of automation and efficiency in their geospatial work.
ModelBuilder empowers GIS professionals to create efficient, automated workflows by visually connecting geoprocessing tools, variables, and data sources. This tool not only streamlines processes but also ensures reproducibility and documentation of spatial analyses. As GIS continues to play a vital role in various industries, ModelBuilder serves as a valuable asset for professionals seeking to harness the power of automation and efficiency in their geospatial work.